In November 1979, Atari released a popular arcade shooter game Asteroids. The player controls a single spaceship in an asteroid field periodically traversed by flying saucers. It shoots down asteroids and other obstacles simultaneously, not trying to get hit. We may have that technology soon.
The Mission Possible
NASA would crash a multimillion-dollar spacecraft into an asteroid. DART or Double Asteroid Redirection Test aimed to test a method of planetary defense against near-Earth objects. It was one of its kind in all of human history. Dart was designed to assess how much a spacecraft impact deflects an asteroid through a transfer of momentum by hitting it head-on and attempting to slow it. By changing the trajectory, the asteroid would miss the earth.
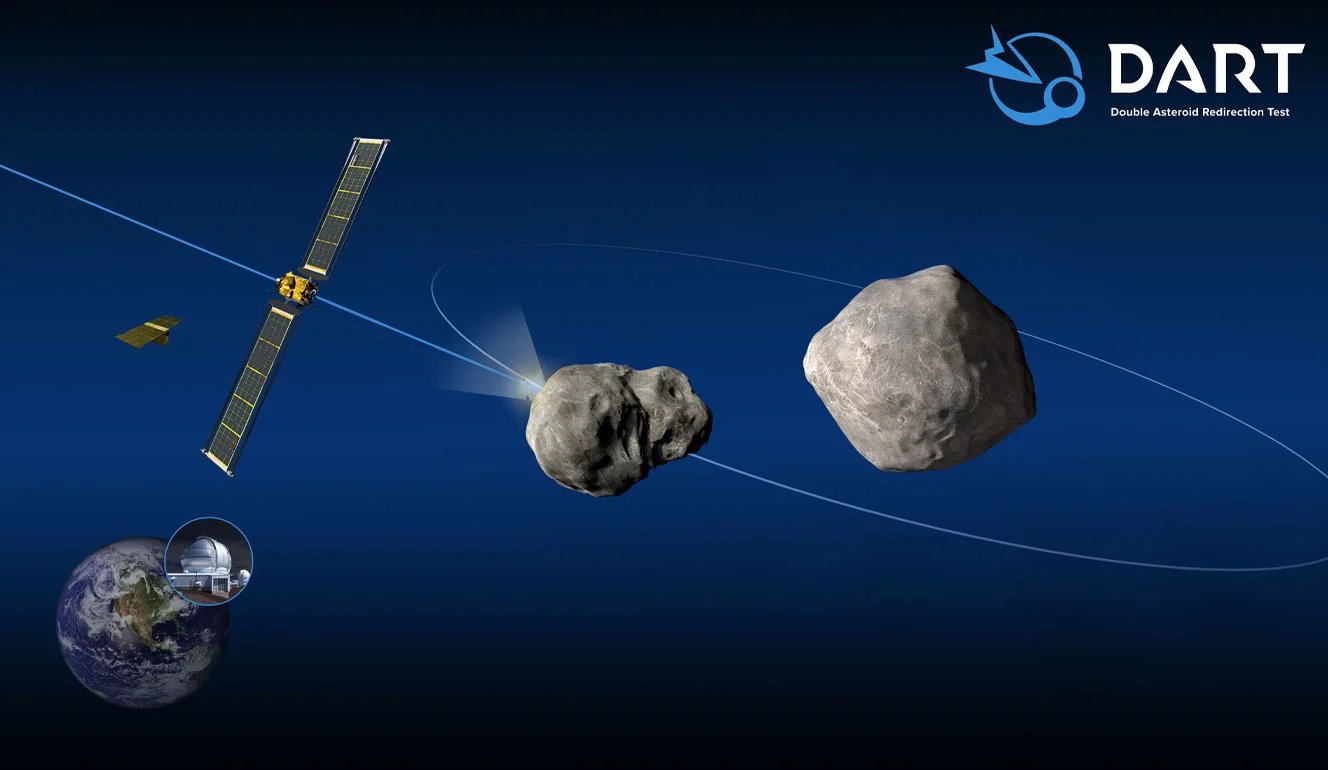

The target is the ‘moon’ of a binary asteroid system of 65803 Didymos named Dimorphous. Of course, this asteroid is not colliding with earth. By observing the orbit of Dimorphic, we can measure the effect of impact.
Asteroids are minor planets of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
Although the likelihood of an asteroid hitting the earth is slim, it is still a real possibility. There are several movies with this plot, like Don’t Look Up, Deep Impact, and Armageddon, although popular but inaccurate.
The Trek
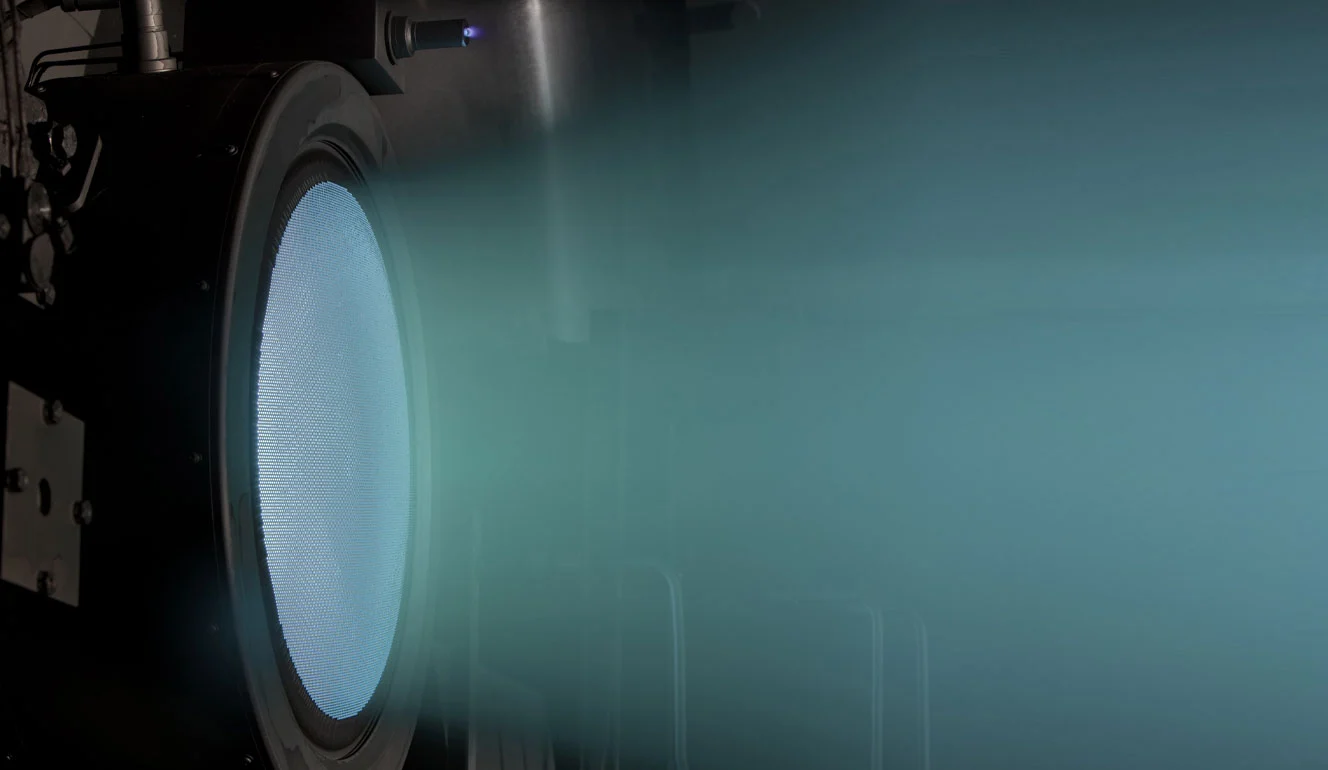
NASA launched DART from the Vandenberg Space Force Base on November 24, 2021, using Elon Musk’s SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. DART’s interplanetary flight to Dimorphos took nine months, and the NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster (NEXT) project propelled the spacecraft across 17.5 km of space. This gridded electrostatic ion thruster is about three times as powerful as the NSTAR used on Dawn and Deep Space 1 spacecraft.
Because of the enormous distance, NASA could not guide the DART remotely, and by using the onboard Smart NAV system, the spacecraft did not get lost in space but showed itself to the target.
Deep Impact
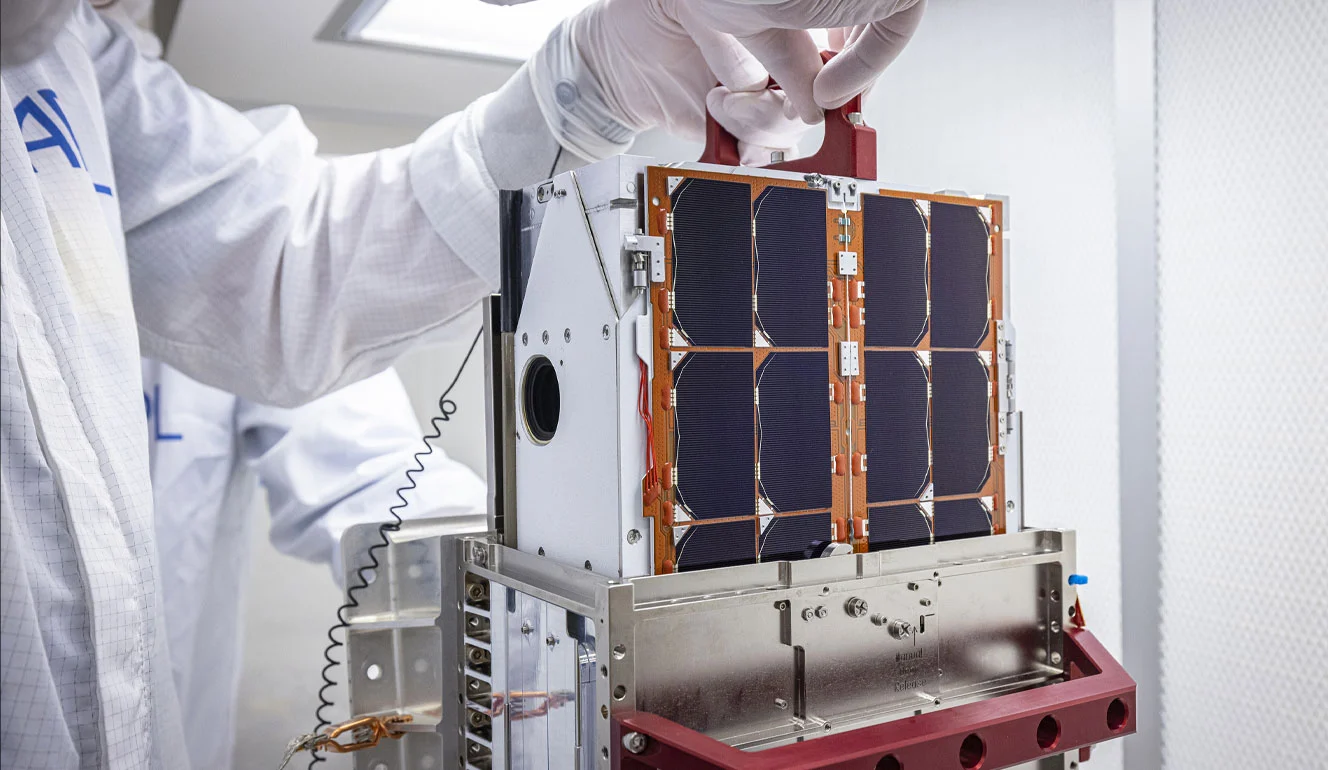

Upon reaching 65803 Didymos, DART was already traveling 6.6 km per second. There are two spacecraft, the DART impactor, the actual craft that hit the asteroid. The other is LICIACube or the Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids. Before impact, this will detach from DART and make observations.
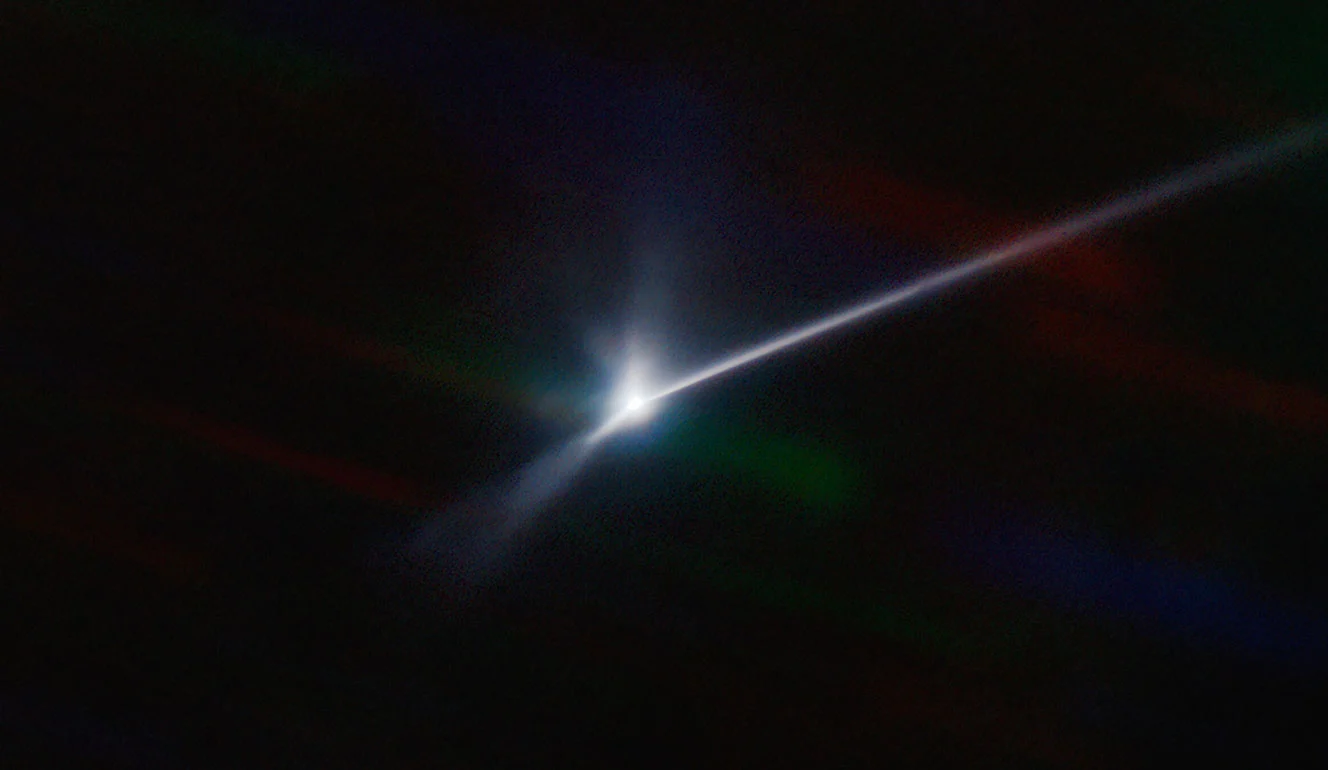

On September 22, 2022, the DART Impactor hit Dimorphos with the kinetic energy of 11 gigajoules or three tones of TNT. The impact was recorded by the LICIACube, the James Webb Telescope, and other space and ground-based telescopes. They saw a beautiful dust trail coming out like a comet.
The Result
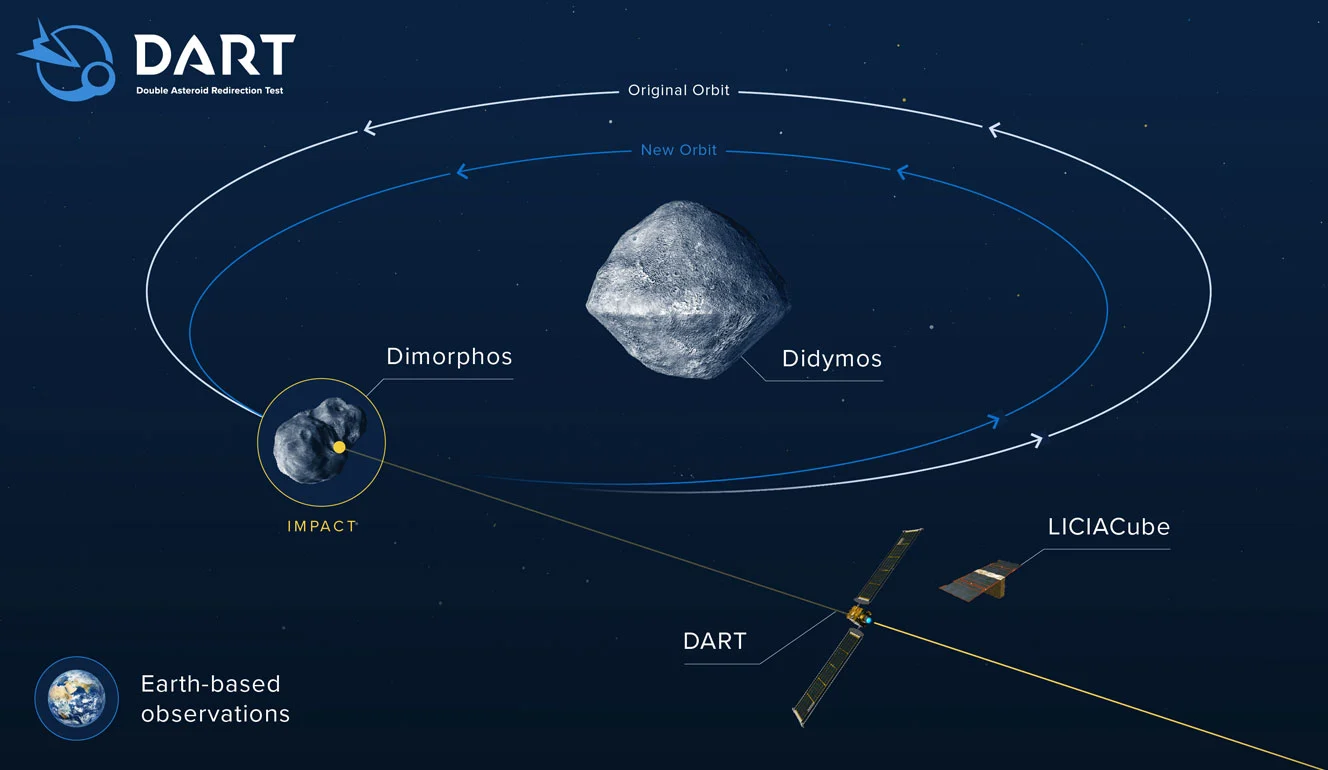
After the impact, NASA hoped Dymorphos would change its orbit for about three minutes. But observation shows that the orbit was shortened by 32 minutes. The mission’s success was enormous.
The Future Mission
The mission would use the data collected to create a planetary defense against celestial objects like asteroids and comets.There are future missions to test other ways of planetary defense. If the object is enormous, a thermonuclear explosion can nudge it. There is also the gravity tractor, where you park a spacecraft near an object and, using gravity, gently pull the thing off its trajectory.
So, shields up!